If you’re serious about SEO, knowing how to create sitemap XML is more than just a technical task — it’s a strategic advantage.
Sitemaps are often overlooked or treated as a “set it and forget it” tool. But in reality, they play a crucial role in helping search engines discover, crawl, and index your content efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about how to create sitemap XML like a pro — from basic setup to advanced optimization strategies that can improve your site’s performance in search results.
What Is XML Sitemap?
An XML sitemap is a file that lists all the important URLs of your website in a format that search engines like Google can easily read. It helps crawlers understand your site structure and prioritize which pages to index.
While not every site absolutely needs one (Google can usually find your pages via internal links), having a well-structured sitemap gives you more control over what gets indexed — especially for large sites, new websites, or those with complex navigation.
Why Creating a Sitemap XML Matters for SEO
Knowing how to create sitemap XML is essential for several reasons:
- Improved crawl efficiency : Helps Google discover new and updated pages faster.
- Better indexation : Ensures critical pages aren’t missed due to poor internal linking.
- Control over priorities : You can indicate which pages are most important using
<priority>and<changefreq>. - Error tracking : Makes it easier to monitor crawl errors and indexing issues in tools like Google Search Console.
Think of your sitemap XML as a roadmap for search engines — the better organized it is, the smoother the journey for bots.
Step-by-Step: How to Create Sitemap XML Manually
Creating an XML sitemap manually gives you full control over its contents and structure. Here’s how to do it:
Tools Needed:
- A text editor (like Notepad++, VS Code, or Sublime Text)
- Basic knowledge of XML syntax
Sample XML Sitemap Structure:
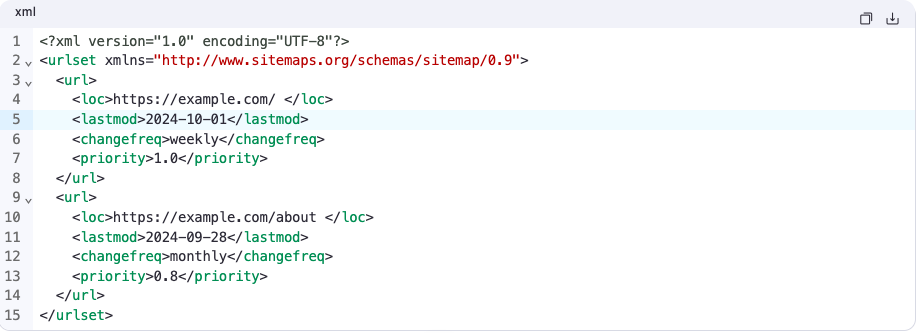
Steps:
-
- Open a blank document in your text editor.
- Paste the above code and replace the example URLs with your own.
- Save the file as
sitemap.xml. - Upload it to your root directory (e.g.,
https://example.com/sitemap.xml).

This method works best for small sites or when you want complete control over which URLs are included.
How to Create Sitemap XML Automatically (Best Tools & Plugins)
For most websites — especially larger ones — manually creating sitemap XML isn’t practical. Fortunately, there are powerful tools and plugins that make it easy to generate sitemap XML automatically.
Top Tools to Generate Sitemap XML:
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider – Crawl-based sitemap generator for technical audits.
- Ahrefs Site Audit – Automatically creates sitemaps and highlights issues.
- SEMrush Site Audit – Generates sitemaps and integrates them into SEO reports.
- Google Search Console – Lets you view and submit sitemaps directly.
Best WordPress Plugins to Make Sitemap XML:
- Yoast SEO – Automatically generates and updates sitemaps.
- RankMath – Lightweight alternative with smart sitemap generation.
- Google XML Sitemaps (Classic Plugin) – Still reliable for legacy sites.
For Non-WordPress Sites:
- Shopify : Automatically generates sitemaps at
/sitemap.xml. - React/Vue/Next.js : Use tools like
sitemap.jsor server-side rendering to generate dynamic sitemaps. - Headless CMS : Integrate with static site generators (e.g., Gatsby, Hugo) to build sitemaps during deployment.
Using these tools ensures your sitemap stays up-to-date without manual intervention.
Advanced Tips: How to Make Your Sitemap XML Work Harder for SEO
Once you know how to create sitemap XML, it’s time to take things further. Here are some pro-level strategies to optimize your sitemap strategy.
Segment Your Sitemap by Content Type
Break down your sitemap into smaller files:
/sitemap-posts.xml/sitemap-products.xml/sitemap-pages.xml
This makes it easier to manage and improves crawl prioritization.
Prioritize High-Value Pages
Use the <priority> tag to tell Google which pages matter most:

Exclude Low-Value URLs
Avoid including:
- Duplicate content
- Internal search pages
- Session IDs or filter URLs
- Noindexed pages
These clutter your sitemap and waste crawl budget.
Handle Large Websites with Sitemap Indexes
If your site has more than 50,000 URLs or your sitemap exceeds 50MB, use a sitemap index file:
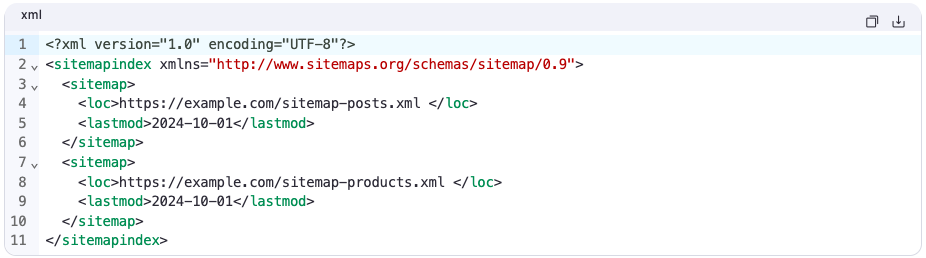
This keeps everything organized and scalable.
Submit Sitemap XML to robots.txt
Make sure your sitemap is linked in your robots.txt file:

This tells Google where to find your sitemap.
How to Submit XML Sitemap to Google Search Console
After learning how to create sitemap XML, the next step is submitting it to Google.
Step-by-Step:
- Go to Google Search Console .
- Select your property.
- Click on Sitemaps in the left-hand menu.
- In the “Add a new sitemap” field, enter:

or

5. Click Submit .
Monitor Performance:
- Check Index Coverage to see if Google is successfully reading your sitemap.
- Review Crawl Stats to ensure no major drops after submission.
- Watch for errors , warnings, or exclusions.
This helps you identify and fix any issues before they impact your rankings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues When You Create Sitemap XML
Even experienced SEOs run into problems when generating sitemap XML. Here are the most common issues and how to fix them.
Issue |
Cause |
Fix |
| Invalid XML Format | Missing tags, incorrect syntax | Validate with W3C validator or online tools |
| Sitemap Not Found (404) | Incorrect upload path | Ensure it’s uploaded to root directory |
| Blocked by robots.txt | Disallowed in robots.txt | Remove disallow rule |
| Too Many URLs | Exceeds 50,000 entries | Split into multiple sitemaps |
| Duplicate Entries | Same URL listed multiple times | Clean up and consolidate |
Bonus: How to Find XML Sitemap on Site (Even If It’s Hidden)
Sometimes you need to locate a sitemap but don’t have access to the backend. Here’s how to find XML sitemap on site:
Quick Methods:
- Check
robots.txt: Visithttps://example.com/robots.txtand look forSitemap:lines. - Try default paths:
https://example.com/sitemap.xmlhttps://example.com/sitemap_index.xml
- Use Screaming Frog to crawl homepage and extract sitemap link.
- Use online tools like XML Sitemap Finder .
This is especially useful when auditing competitor sites or taking over unfamiliar projects.
Pro Techniques: Automating and Optimizing Your Sitemap Strategy
The pros don’t just create sitemap XML once — they automate and refine their strategy continuously.
Automate Updates:
- Use CI/CD pipelines to regenerate sitemaps on content updates.
- Set up scripts to auto-upload sitemaps to your server.
- Integrate with headless CMS platforms for real-time updates.
Monitor Health:
- Use tools like Monitor Backlinks or Botify to track sitemap status.
- Log analysis tools help verify if Google is actually crawling your sitemap.
Build Dashboards:
- Combine sitemap data with crawl stats and index coverage in SEO dashboards.
- Visualize trends and catch anomalies early.
Automation and monitoring ensure your sitemap remains accurate and effective long after creation.
Conclusion: Don’t Just Create Sitemap XML — Optimize It
Learning how to create sitemap XML is just the beginning. To truly level up your SEO game, treat your sitemap as a strategic asset — not just a file.
From segmenting sitemaps by content type to automating updates and integrating with analytics, the way you handle your sitemap can significantly impact your site’s visibility and crawlability.
So go beyond the basics. Audit your current sitemap strategy. Refine it. Optimize it. And watch your site climb higher in search results.


